JonesX Mission: SULTAN Graphing Activity
Welcome to the SULTAN graphing activity! As part of your JonesX mission, you’ve conducted a reaction time experiment. Now it’s time to graph your data using Scale, Units, Labeling, Titles, Accuracy, and Neatness. Use this activity to learn and review each principle.
1. Scale
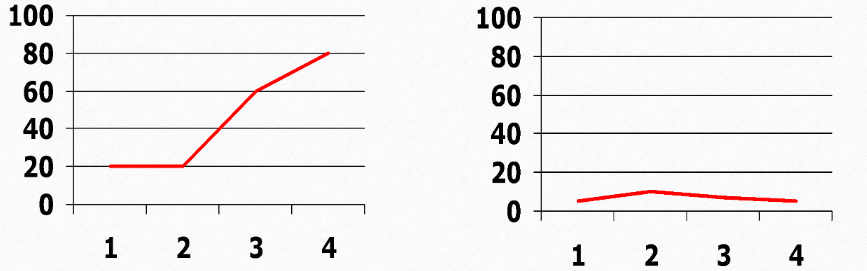
For your notes (Scale):
- Choose a scale that includes all reaction times.
- Avoid crowding or stretching the data.
- Ensure the scale fits the graph space well.
Think about why choosing the right scale is important. How does it affect the readability of your data?
2. Units
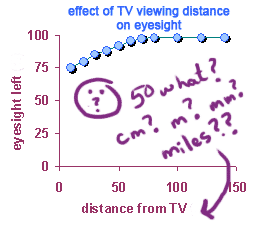
For your notes (Units):
- Include the correct units on both axes.
- Units ensure clarity in understanding the data.
- For time, use “seconds” (s) on the graph.
Consider which units you used in your experiment. Why is it important to label them correctly?
3. Labeling
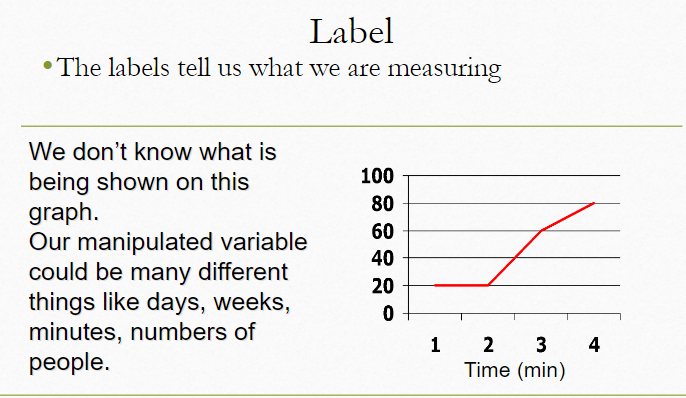
For your notes (Labeling):
- Label both axes clearly.
- X-axis: what was tested (e.g., stimuli type).
- Y-axis: what was measured (e.g., reaction time in seconds).
Think about why labeling is crucial. What would happen if your graph had no labels?
4. Titles
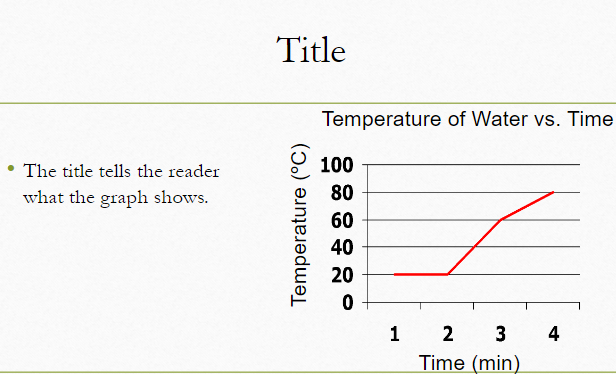
For your notes (Titles):
- Write a clear, informative title.
- The title should summarize the graph’s purpose.
- Example: “Reaction Time Comparison Under Different Conditions.”
Why is a title important for your graph? How does it help in understanding the data?
5. Accuracy
For your notes (Accuracy):
- Ensure data points are plotted correctly.
- Check that the scale and units match the data.
- Review your graph for errors before finalizing.
Why is it important to check the accuracy of your graph? How can errors impact the results?
6. Neatness

For your notes (Neatness):
- Keep your graph clear and easy to read.
- Ensure lines, labels, and text are legible.
- Present your graph neatly to avoid confusion.
Why is neatness important in presenting your graph? How does it affect readability and interpretation?
Common Problems

For your notes (Common Problems):
- Incorrect scaling leading to distorted data.
- Missing labels making the graph unclear.
- Inaccurate plotting causing misleading information.
- Using a graph type that does not reveal patterns in the data.
What are some common issues you might encounter when graphing, and how can you avoid them?
Activity Completed!
Congratulations on completing the SULTAN graphing activity! You’ve learned about Scale, Units, Labeling, Titles, Accuracy, and Neatness. Make sure to review your notes and apply these principles to your graphing tasks.
Unique Code for Verification:
